The Royal Commission identified 10 critical elements that are necessary to create a safe environment for children and young people. These elements became the 10 Child Safe Standards and are essential to creating a Child Safe Organisation.
Each State and Territory Government is responsible for implementing legislation to embed and/or monitor compliance of the Child Safe Standards and/or the National Principles. We provide a summary of the recent legal developments below (as of August 2024).
New South Wales
Legislation: Children’s Guardian Act 2019 (NSW)
- Regulation of the Child Safe Standards.
- Read about the NSW child safe standards.
Victoria
Legislation: Child Wellbeing and Safety Act 2005 (Vic)
- In Victoria there are 11 Child Safe Standards.
- The new Child Safe Standards replaced Victoria’s 7 Standards and Principles.
- Read about the Victorian child safe standards.
South Australia
Legislation: Children and Young People (Safety) Act 2017 (SA)
- The South Australian government has implemented the Child Safe Environments Program.
- Child related organisations are required to align child safe policies and procedures with the National Principles for Child Safe Organisations.
- Read about the South Australia child safe standards.
Tasmania
Legislation: Child and Youth Safe Organisations Act 2023 (Tas)
- Organisations that engage with children and young people are required to implement the 10 Child and Youth Safe Standards.
- Read more at - Child and Youth Safe Organisations Framework | CARCRU (justice.tas.gov.au)
Australian Capital Territory (ACT)
Legislation: Human Rights Commission Act 2005 (ACT)
- From 1 August 2024, it is mandatory for all organisations that provide services for children and young people to implement the ACT Child Safe Standards Scheme.
- Read more at ACT Child Safe Standards Scheme - HRC
What is happening in the other States and Territories?
- The QLD government introduced the Child Safe Organisations Bill 2024 (QLD) to require child-related organisations to implement the Child Safe Standards framework. Regulation of the Child Safe Standards is pending in QLD. For more information refer to Growing child safe organisations.
- The WA and the NT are in the process of developing a regulatory scheme to monitor the Child Safe Standards.

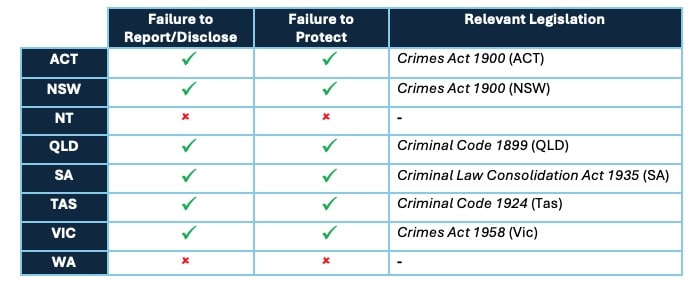
Child Safe Legal Obligations – Criminal Offences
Criminal Offences
A criminal offence is a crime against the State (or government). A crime occurs when a person breaks a law and commits an offence against the community in general or against a particular victim. We outline some criminal offences that apply to Swim Schools (and their staff) in the Australian States and Territories below.
- Failure to Report/Disclose
The Failure to Report/Disclose offence imposes a responsibility on all adults to make a report to Police, if they have knowledge that a child abuse offence has been committed against a child or young person.
2. Failure to Protect
The Failure to Protect offence imposes responsibility on all adults engaged in child-related work to ensure that the children and young people under the care of the organisation are protected from risks of harm and abuse.
Child Safe Legislation in each Australian State and Territory
Screenshot
What this Means for Swim Schools
- Swim Schools and its staff must be aware of and comply with the child safe legal obligations (criminal offences) relevant to their State or Territory.
- Swim Schools in ACT, NSW, South Australia, Tasmania and Victoria must comply with the Child Safe Standards and/or the National Principles.
- Swim Schools in QLD, NT and WA should prepare for upcoming regulation of the Child Safe Standards by implementing child safety measures and working towards compliance.
How can Child Safeguard help you
If you have any questions or would like to learn how Child Safeguard can help your Swim School comply with the Child Safe Standards and meet your child safe legal obligations, please feel free to get in touch by email at: monique.frendo@childsafeguard.com.au
Child Safe Training is a must for everyone, get started with online training modules.





